
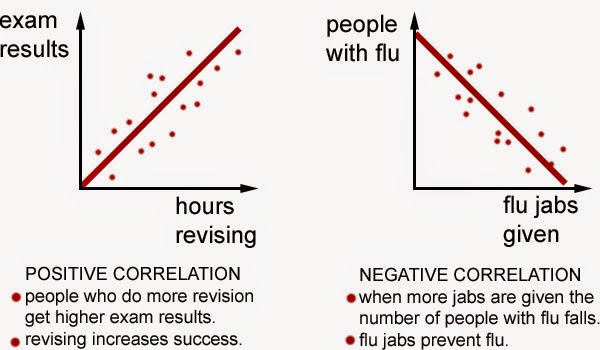
#A negative correlation exists between professional#
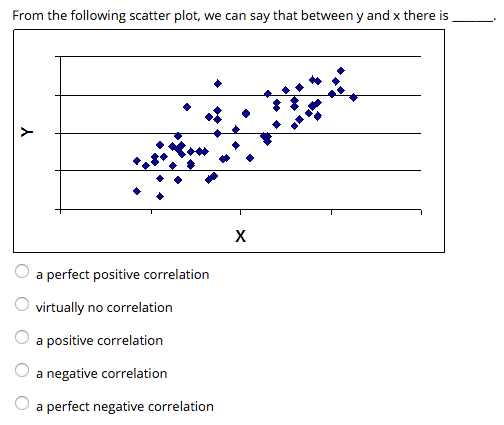
Tutors, instructors, experts, educators, and other professionals on the platform are independent contractors, who use their own styles, methods, and materials and create their own lesson plans based upon their experience, professional judgment, and the learners with whom they engage. Varsity Tutors connects learners with a variety of experts and professionals. In statistics, a perfect negative correlation is. Varsity Tutors does not have affiliation with universities mentioned on its website. Negative correlation is a relationship between two variables in which one variable increases as the other decreases, and vice versa. Media outlet trademarks are owned by the respective media outlets and are not affiliated with Varsity Tutors.Īward-Winning claim based on CBS Local and Houston Press awards. negative correlation is a relationship between two variables in which an increase in one variable is associated with a. The relationship is neither linear nor monotonic.Names of standardized tests are owned by the trademark holders and are not affiliated with Varsity Tutors LLC.Ĥ.9/5.0 Satisfaction Rating based upon cumulative historical session ratings through 12/31/20. The three types of scatterplots are the following kinds: positive correlation scatterplot (follows a positive linear function), negative association scatterplot (follows a negative linear. Even though the relationship between the variables is strong, the correlation coefficient would be close to zero. This example shows a curved relationship. The Pearson correlation coefficient for these data is 0.843, but the Spearman correlation is higher, 0.948. This relationship is monotonic, but not linear. Negative r values indicate a negative correlation, where the values of one variable tend to increase when the values of the other variable decrease. This plot shows both variables increasing concurrently, but not at the same rate. In a linear relationship, the variables move in the same direction at a constant rate. In a monotonic relationship, the variables tend to move in the same relative direction, but not necessarily at a constant rate. The relationship is negative because, as one variable increases, the other variable decreases. The points fall close to the line, which indicates that there is a strong negative relationship between the variables. There is not enough information to determine what type of correlation exists between variables R and S. No correlation exists between variables R and S. The relationship is positive because as one variable increases, the other variable also increases. A negative correlation exists between variables R and S. The points fall close to the line, which indicates that there is a strong linear relationship between the variables. Some points are close to the line but other points are far from it, which indicates only a moderate linear relationship between the variables. The points fall randomly on the plot, which indicates that there is no linear relationship between the variables. Spearman's correlation coefficient is appropriate for monotonic forms. The Pearson correlation coefficient is appropriate for linear forms. The linear correlation coefficient is a unitless measure of. So r close to 0 does not imply a relation, just no linear relation. If r is close to 0, then little or no evidence exists of a linear relation between the two variables. The following are examples of the types of forms that the correlation coefficients describe. The closer r is to 1, the stronger is the evidence of negative association between the two variables. Outliers can heavily influence the results for the Pearson correlation coefficient.ĭetermine whether the relationships are linear, monotonic, or neither.
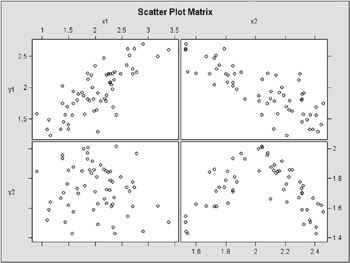
Also, look for outliers in the relationships. Use the matrix plot to examine the relationships between two continuous variables.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
